Functions of different parts of the brain – Delve into the intricate world of the human brain and unravel the remarkable functions of its diverse regions. From cognition and memory to coordination and emotion, each part of the brain plays a vital role in shaping our thoughts, actions, and experiences.
Explore the intricate workings of the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, limbic system, and basal ganglia, as we uncover their unique contributions to our neurological symphony.
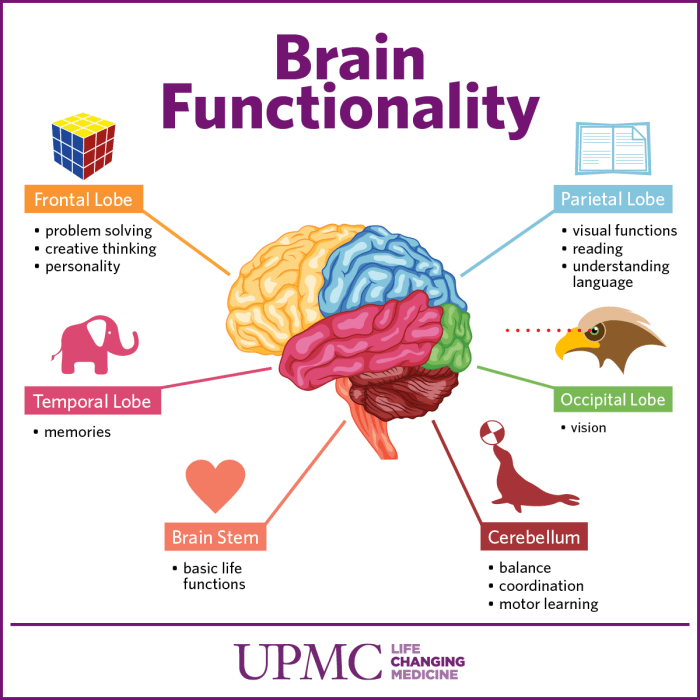
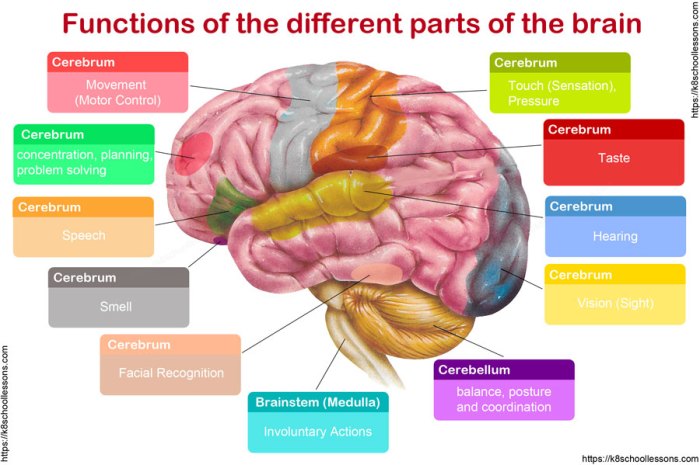
Cerebrum
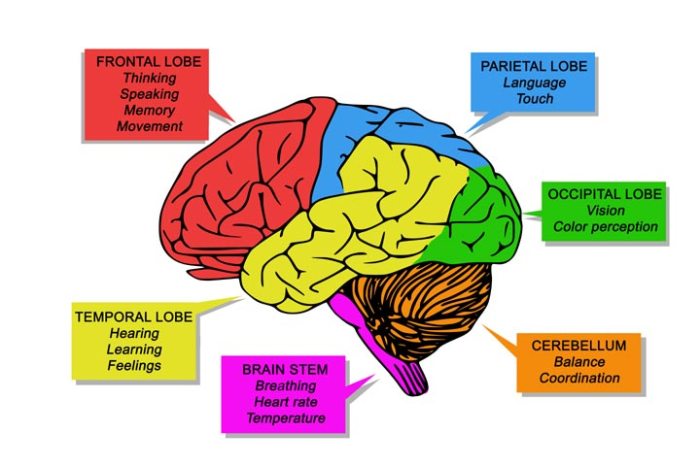
The cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, is responsible for higher-level functions such as cognition, memory, and language. It is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, which are connected by a thick band of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum.
The cerebrum is composed of four lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe has specific functions:
Frontal Lobe
- Executive function: planning, decision-making, problem-solving
- Motor function: controlling voluntary movement
- Language production: Broca’s area
Parietal Lobe
- Sensory processing: touch, temperature, pain
- Spatial awareness: understanding the relationship between objects in space
- Mathematical abilities
Temporal Lobe
- Auditory processing: hearing
- Memory: hippocampus
- Language comprehension: Wernicke’s area
Occipital Lobe, Functions of different parts of the brain
- Visual processing: seeing
- Color perception
- Motion detection
The cerebrum processes information by receiving sensory input from the body and sending motor commands to the muscles. It also stores memories and controls higher-level cognitive functions such as thinking, reasoning, and decision-making.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, is responsible for coordinating and regulating movement, balance, and posture. It receives sensory information from the body, including the muscles, joints, and vestibular system, which is responsible for balance. The cerebellum then uses this information to fine-tune motor commands from the cerebrum, ensuring smooth, coordinated movements.
Functions of the Cerebellum
- Coordination:The cerebellum coordinates the timing and sequence of muscle movements, ensuring smooth and efficient movement.
- Balance:The cerebellum works with the vestibular system to maintain balance and equilibrium. It receives signals from the vestibular system about the head’s position and movement and uses this information to adjust muscle tone and posture.
- Motor control:The cerebellum fine-tunes motor commands from the cerebrum, making movements more precise and accurate.
Brainstem
The brainstem is a vital part of the brain that controls essential functions like breathing, heart rate, and sleep. It also serves as a relay center between the brain and the spinal cord, transmitting sensory and motor information. The brainstem consists of three main parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata.
- Midbrain:The midbrain is located between the cerebrum and the pons. It plays a role in eye movement, hearing, and motor control.
- Pons:The pons is located between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. It helps to regulate sleep, breathing, and swallowing.
- Medulla Oblongata:The medulla oblongata is the lowest part of the brainstem. It controls vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
The brainstem is a critical part of the brain that plays a vital role in our survival. Without the brainstem, we would not be able to breathe, our hearts would not beat, and we would not be able to sleep.
Limbic System
The limbic system is a complex network of brain structures that plays a crucial role in our emotional experiences, motivations, and memory formation. It is located deep within the brain, surrounding the brainstem and thalamus, and includes several key structures, such as the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus.The limbic system is responsible for processing and regulating a wide range of emotions, including fear, anger, joy, and sadness.
It also plays a role in motivation, reward, and punishment, helping us to prioritize our actions and make decisions. Additionally, the limbic system is involved in memory formation, particularly in the formation of new memories and the retrieval of old ones.
Amygdala
The amygdala is a small, almond-shaped structure located deep within the temporal lobes of the brain. It is primarily responsible for processing and regulating emotions, particularly fear and anger. The amygdala receives sensory information from the environment and quickly assesses whether it is threatening or not.
If a threat is detected, the amygdala triggers a fear response, which includes physiological changes such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, as well as behavioral changes such as freezing or fleeing.
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a curved structure located in the medial temporal lobes of the brain. It is primarily responsible for memory formation and retrieval. The hippocampus receives sensory information from the environment and helps to encode it into long-term memory.
It also plays a role in retrieving memories from storage and making them available for conscious recall.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is a small structure located at the base of the brain. It is primarily responsible for regulating homeostasis, which is the maintenance of a stable internal environment within the body. The hypothalamus controls a wide range of physiological functions, including body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, and hormone release.
It also plays a role in motivation and reward, helping us to prioritize our actions and make decisions.
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of interconnected brain structures located deep within the cerebrum. They play a crucial role in motor control, habit formation, and reward processing.The basal ganglia consist of several structures, including the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, and substantia nigra.
Each structure has a specific role in regulating movement and behavior.
Motor Control
The basal ganglia are involved in the planning and execution of movement. They receive input from the cerebral cortex, which sends signals to the basal ganglia about the intended movement. The basal ganglia then process this information and send signals to the thalamus, which in turn sends signals to the muscles to execute the movement.
Habit Formation
The basal ganglia are also involved in the formation of habits. When we repeat a behavior multiple times, the basal ganglia create a neural pathway that makes it easier to perform that behavior in the future. This is why habits can be difficult to break.
Reward Processing
The basal ganglia are also involved in reward processing. When we experience something pleasurable, the basal ganglia release dopamine, a neurotransmitter that makes us feel good. This positive reinforcement motivates us to repeat the behavior that led to the reward.The basal ganglia interact with other parts of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, to regulate movement and behavior.
They are an essential part of the brain’s motor system and play a key role in our ability to learn and adapt to our environment.
Last Word: Functions Of Different Parts Of The Brain
In conclusion, the brain is a masterpiece of nature, a complex organ that governs our every thought, action, and emotion. By understanding the functions of its different parts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the marvels of human consciousness and the boundless potential that lies within.
Common Queries
What is the primary function of the cerebrum?
The cerebrum is responsible for higher-level cognitive functions such as reasoning, planning, language, and memory.
How does the cerebellum contribute to movement?
The cerebellum coordinates muscle movements, ensuring smooth and precise execution.
What vital functions are controlled by the brainstem?
The brainstem regulates essential functions like breathing, heart rate, and sleep.
What role does the limbic system play in emotions?
The limbic system is involved in processing emotions, motivation, and memory formation.
How do the basal ganglia contribute to habit formation?
The basal ganglia are involved in forming habits and routines, as well as reward processing.